In this blog post, Julia Vassileff, BI Consultant and Senior SQL DBA at WARDY IT Solutions, demos the deployment process of Azure Data Factory (ADF) with Azure DevOps.
1. ADF pipeline configuration
For the purpose of this demonstration, I have created ADF pipeline to copy all tables from SQL database onto blob storage.
I have the pipeline developed in adf-demo-dev1 Data Factory and will be deploying code to “adf-demo-uat” and “adf-demo-prod” Data Factories:

It is recommended to integrate all Connections with Azure Key Vault, providing connection details as Secret names. I have created 3 Azure Key Vaults:

and configured Secrets under the same name but different values depending on environment, I have 2 configurations – Blob end point and Azure DB Connection string in each Key Vault:
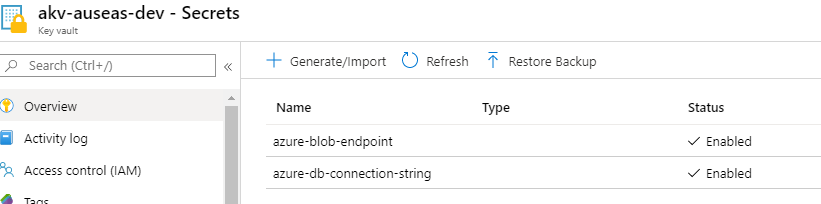
In ADF “adf-demo-dev1” I have configured 3 Connections, 2 Datasets and 1 pipeline:
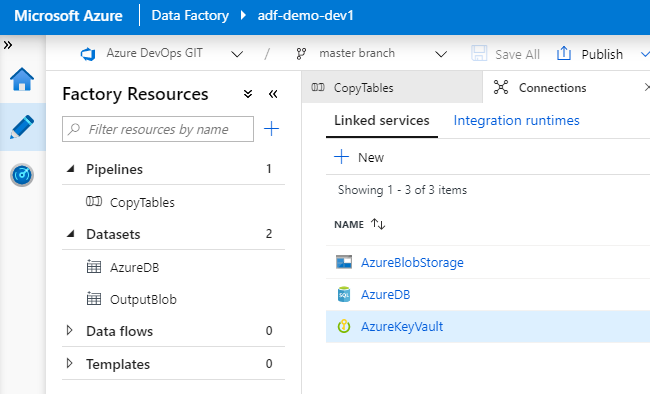
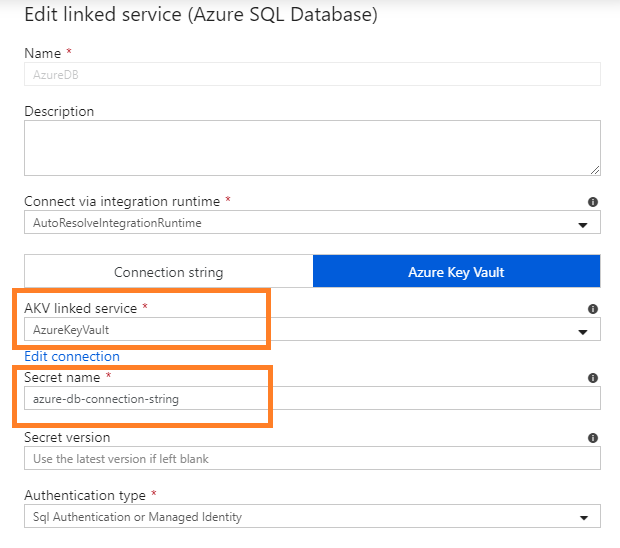
AzureDB and AzureBlobStorage services are integrated with Key Vault, secret names are provided in Linked Service configuration:
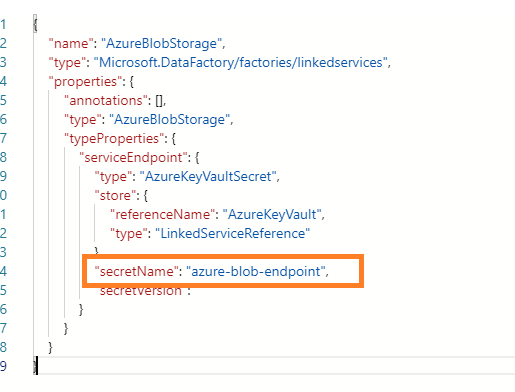
For Blob storage, I modified json file to provide blob end point as Key Vault Secret name:
Key Vault Connection will be changed as part of Release pipeline but AzureDB and Blob Storage configuration will not be changed as Secret names are the same.
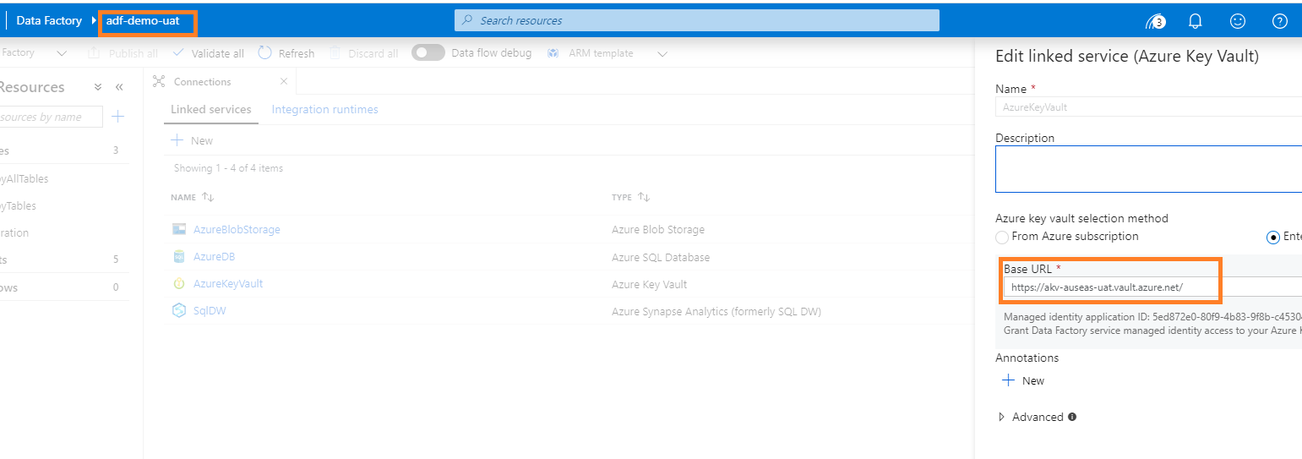
As a prerequisite, I need to grant permissions for UAT ADF to access UAT Key Vault, I do it in the portal:
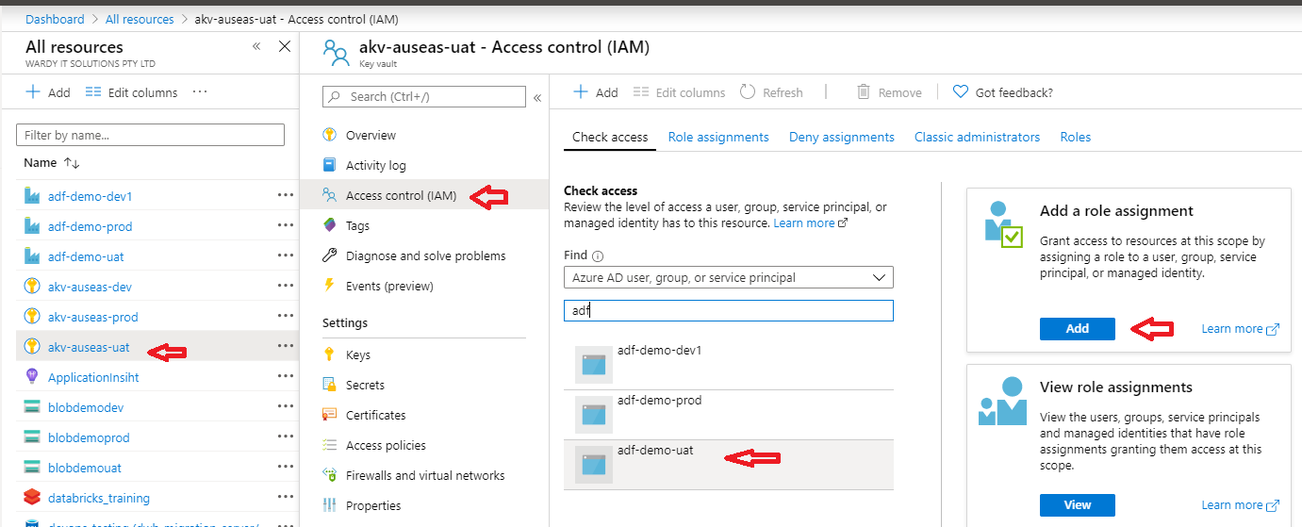
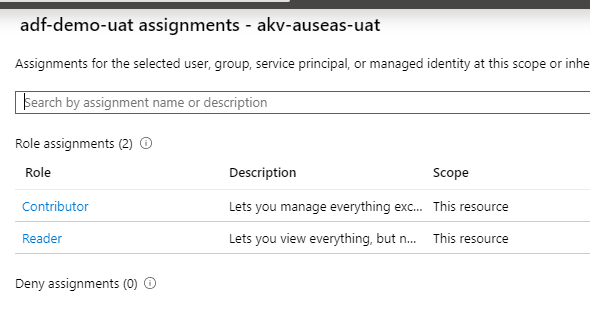
2. DevOps project setup
I connect to DevOps https://dev.azure.com/ and create a new project (ADF Deployment) and Repository. Project can be shared for Database code, ADF code, etc. It is recommended to have a separate Repository for ADF pipeline.
I created a project “ADF Deployment“ and Repository “ADF Deployment“:
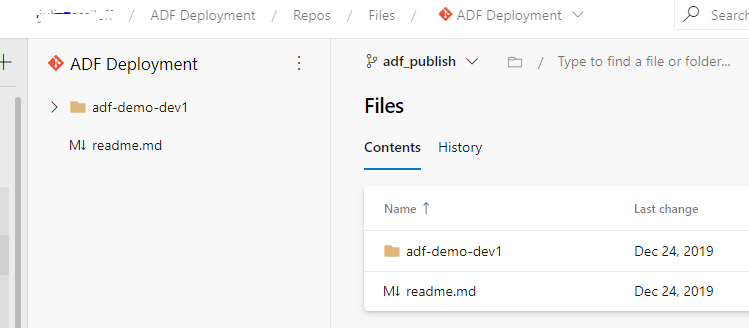
In ADF “adf-demo-dev1“, I configure a link to DevOps repository:
Once we have published ADF pipeline in master branch from UI, adf_publish branch is created in addition to master branch, we can see it in DevOps GUI:
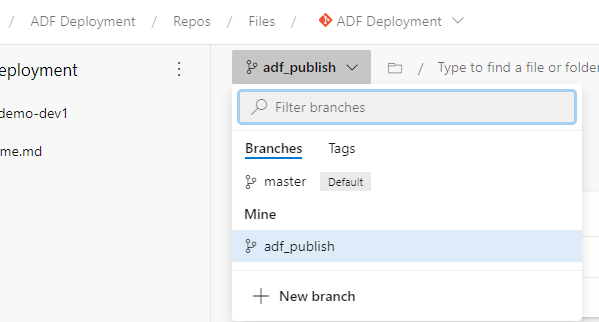
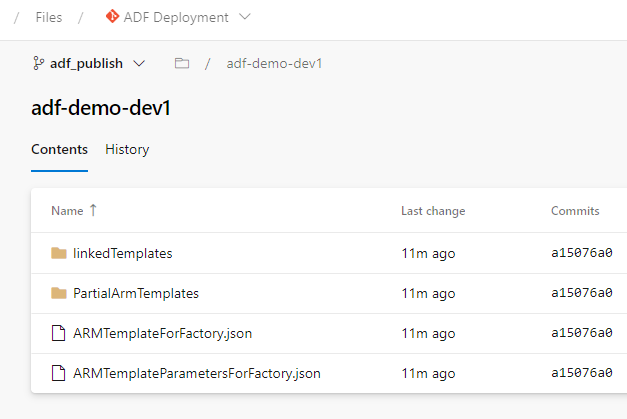
ARM templates are generated in adf_publish branch:
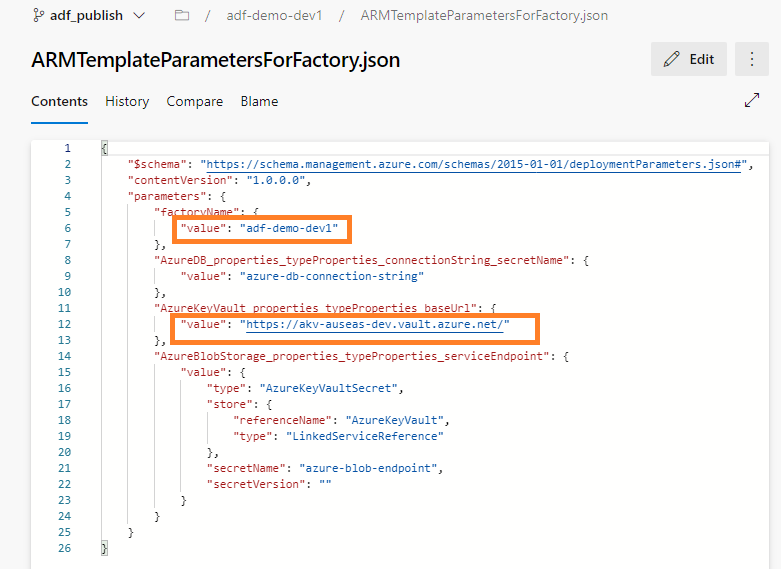
Let’s examine file ARMTemplateParametersForFactory.json, deployment parameters are specified there.
We see Secret names are provided here, we wouldn’t need to change Secret names in Release, but Azure Key Vault base URL and ADF name:
3. Create DevOps Build
The very first step in Automated deployment is to create a Build.
Build will prepare artifacts to be deployed. In case of ADF deployment, we need only to copy ARM template from DevOps onto deployment machine.
Let’s create a Build for ADF deployment:
We will use classic editor to create a pipeline without YAML:
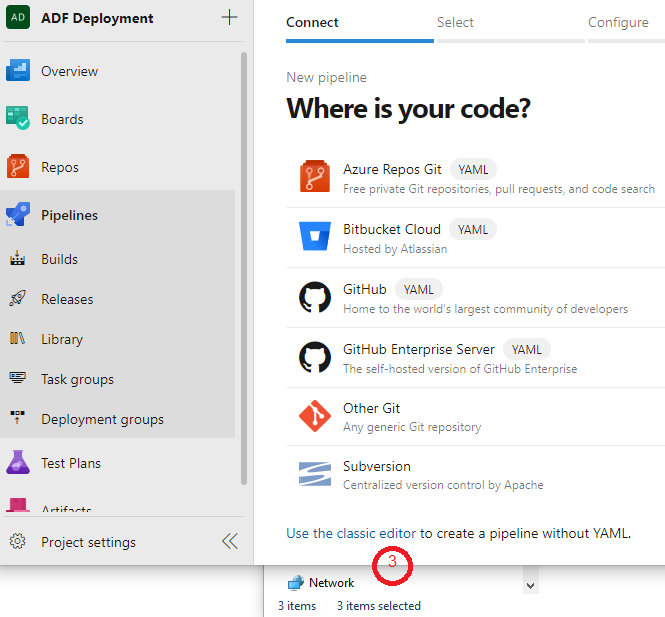
We are selecting adf_publish branch and “Azure Repos Git” as a repository in the Build:
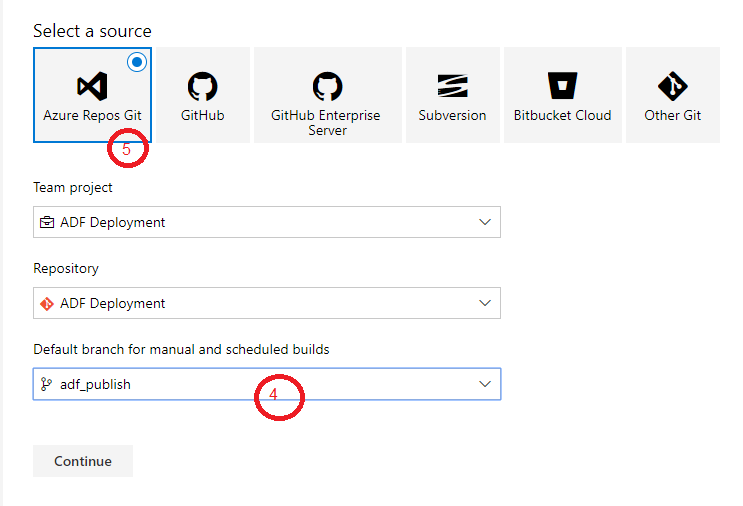
Select “Empty job“:
Agent job is now created:
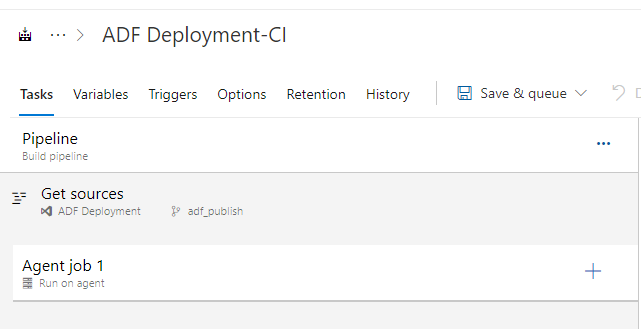
We click “+“ sign to add a task “Publish Pipeline Artifacts“:
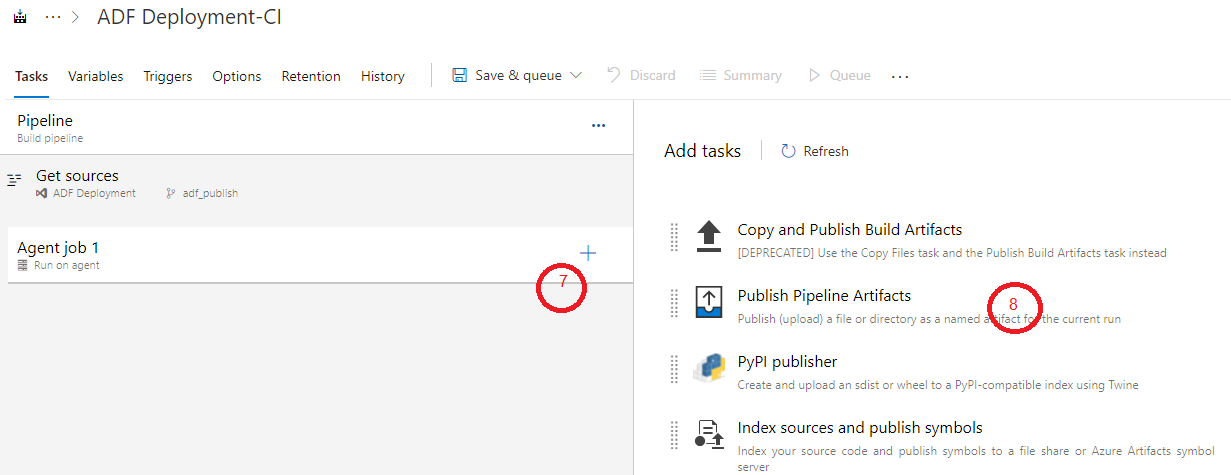
Now we are ready to run Build – “Save and Queue“:
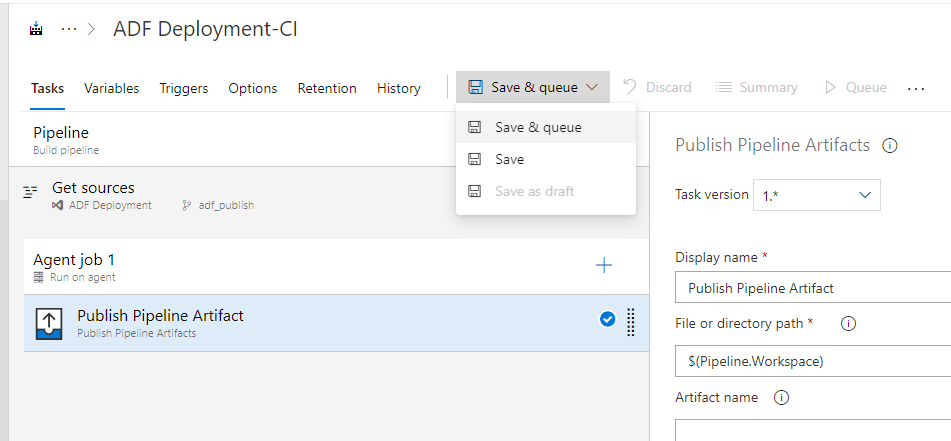
Publish Pipeline Artifacts Save and Queue
4. Create Service Connection
Before we can precede with creating a Release, we need to create a Service connection – this connection will be used by DevOps Agents to connect to the Subscription.
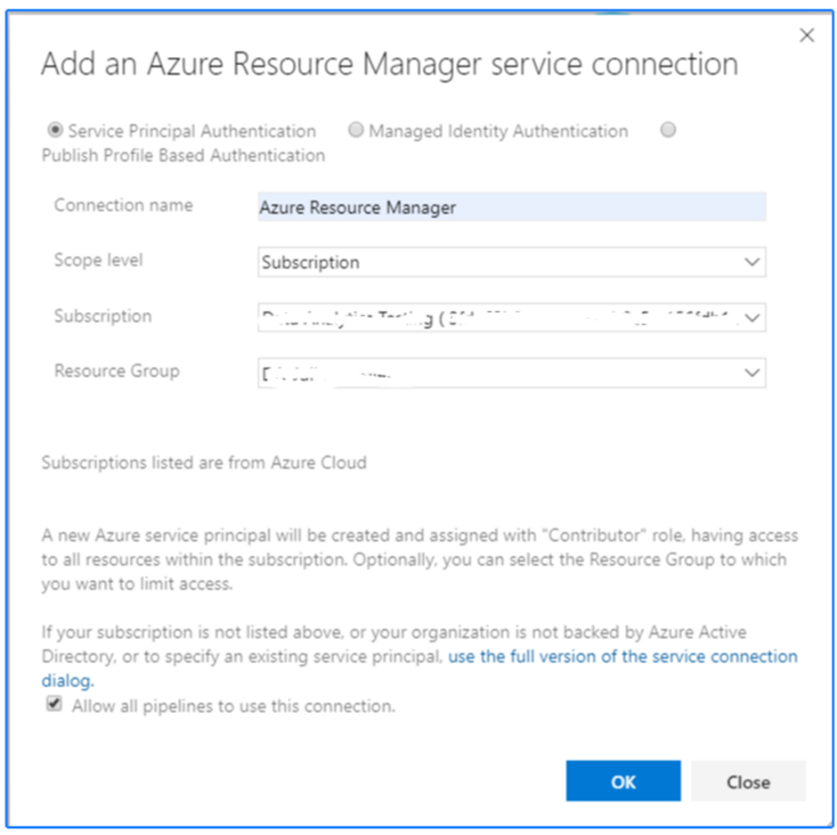
Under project settings select “Service Connections“ I am creating a Service Connection. I have Owner permissions Resource group level, so it works within the group:
creating a Service Connection
5. Create Variables group
Variable groups will be used to define environment (Stage) specific variables. For my deployment, I need to define:
- Data Factory Name : “adf-demo-uat” for UAT Stage and “adf-demo-prod“ for Production
- KeyVaultBaseURL : https://akv-auseas-uat.vault.azure.net/ in UAT and https://akv-auseas-prod.vault.azure.net/ in Production.
I define Variable groups:
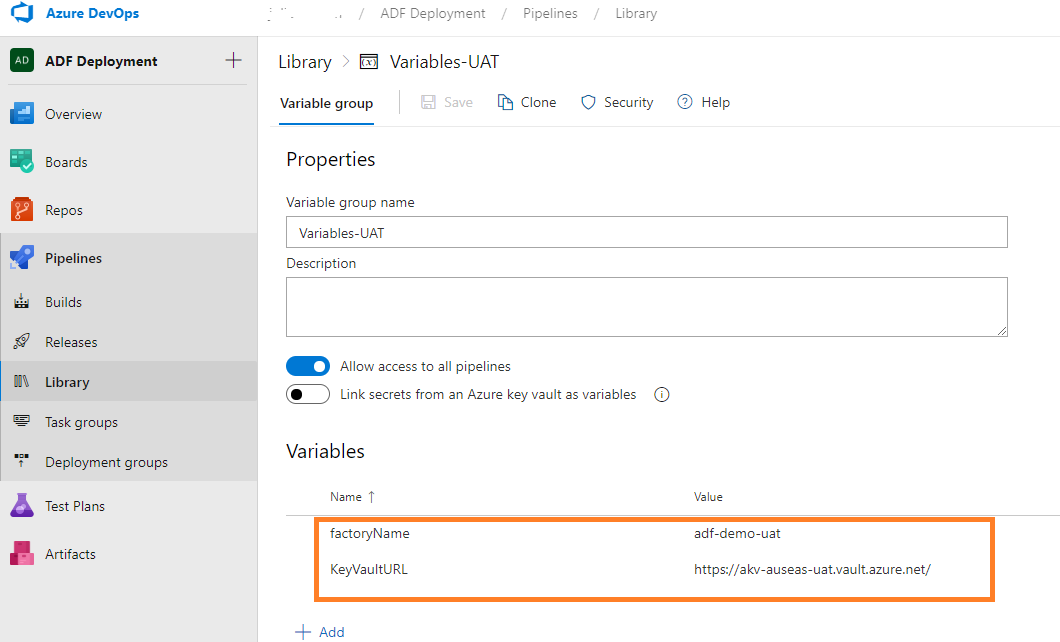
In each Variable group I define variables under the same name:
UAT:
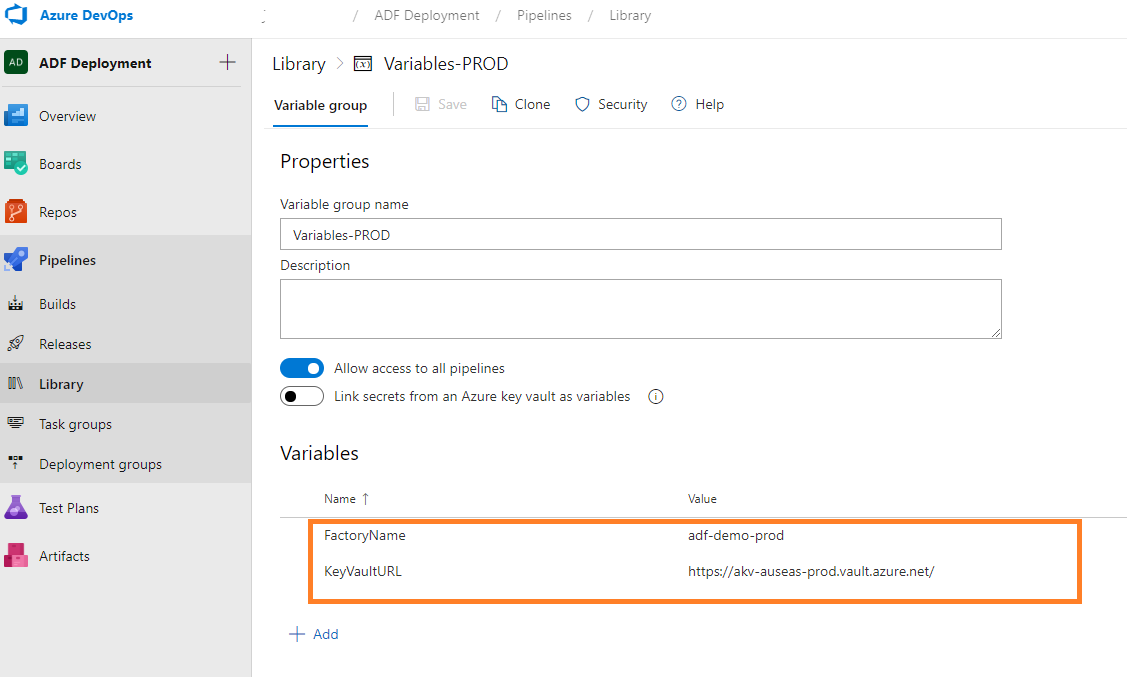
Prod:
6. Create DevOps Release pipeline
Or “Releases“ menu option in left side menu, “New pipeline“

Select “Empty job“ to start building Release pipeline:
Now we have an option to name a Stage. Stage is an environment where we will be deploying to. Let’s name it UAT:
Artifact for Release pipeline is a Build which we just run:
Our Release pipeline looks like below:
Let’s rename it – just type in a new name:
Add a task to UAT Stage:
Select “Azure resource group deployment”:
Rename it as “ADF pipeline deployment”:
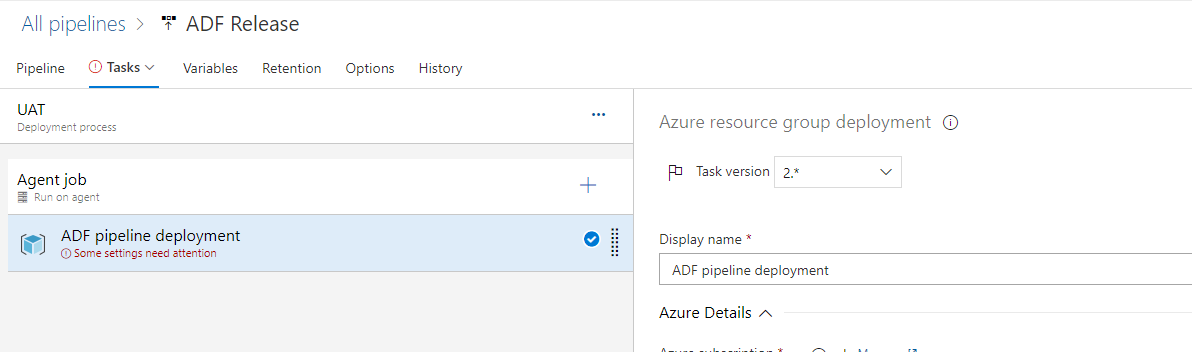
Under “Azure subscription, we select a Service Connection created in pp. 4:
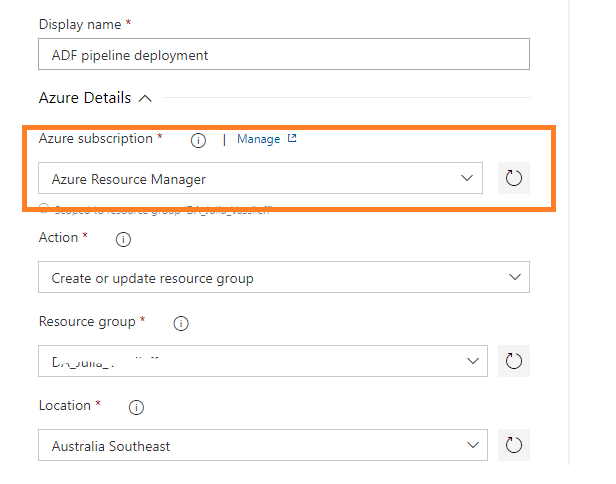
Next section, I need to configure, is Template related:
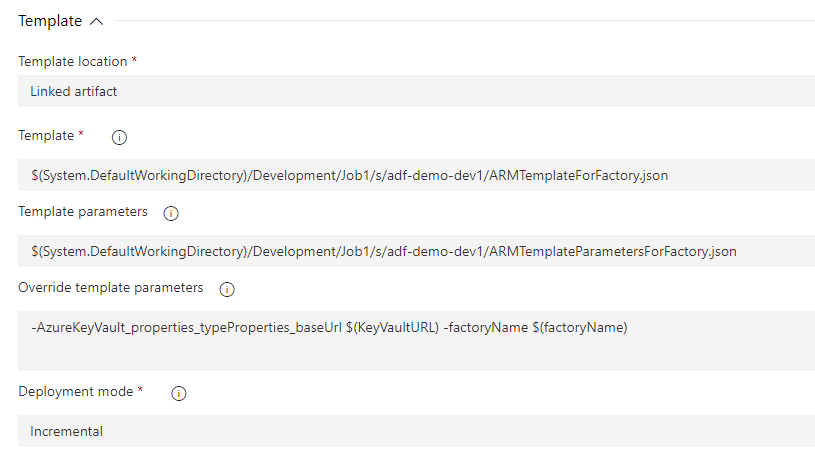
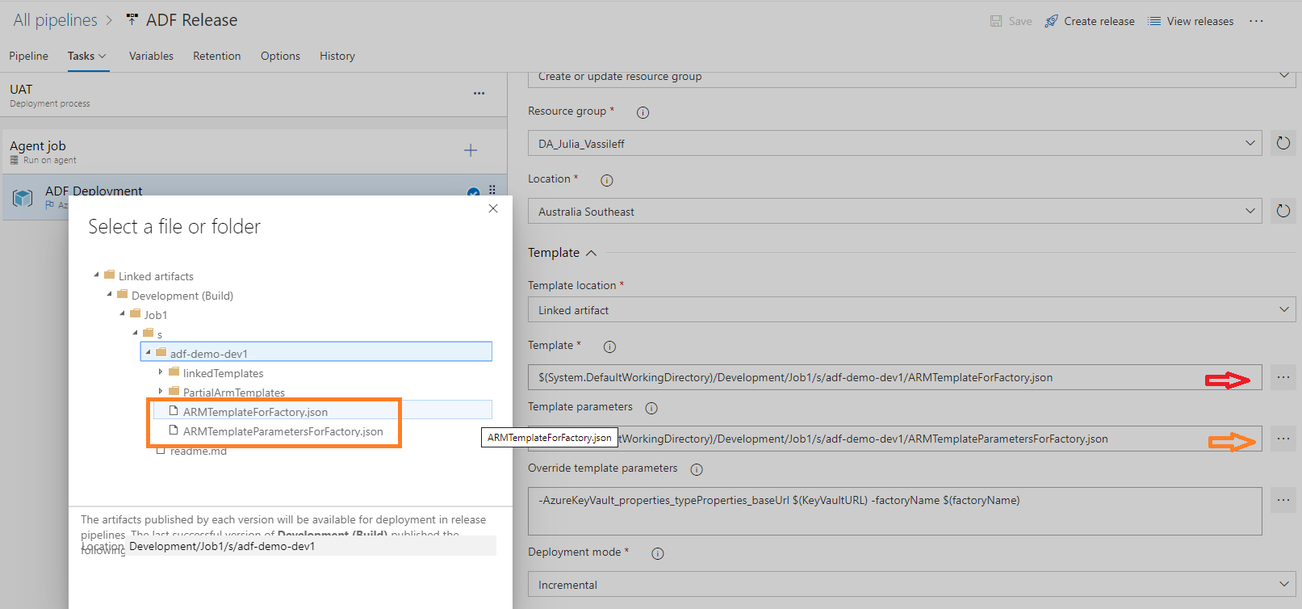
To select Template and Template parameters files, I click on three dots next to the window and navigate to template location:
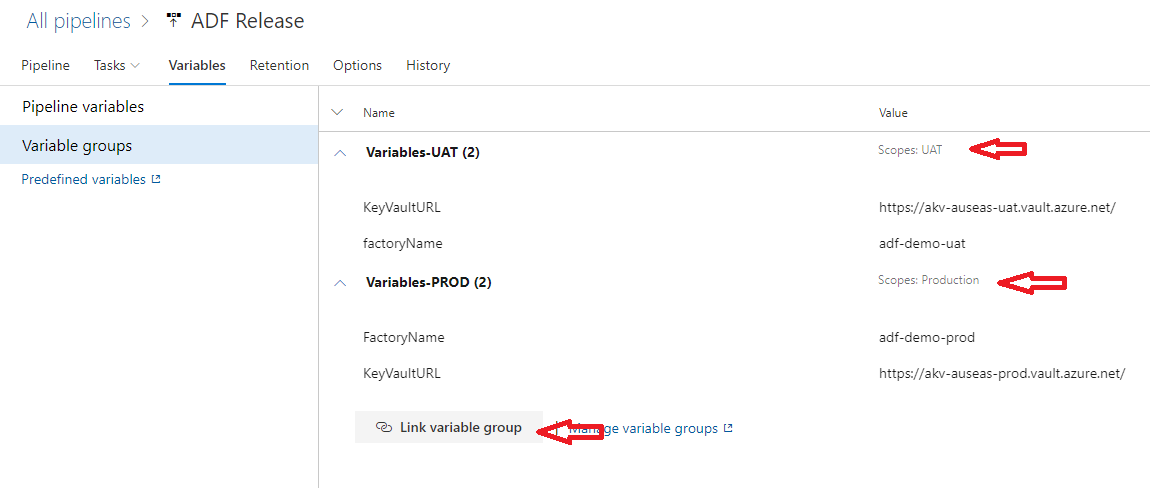
I have linked Variable group with Scope UAT:
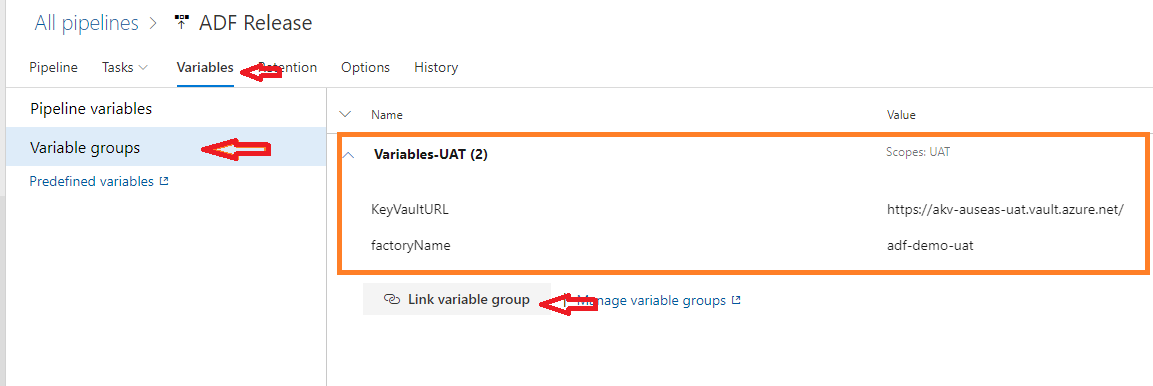
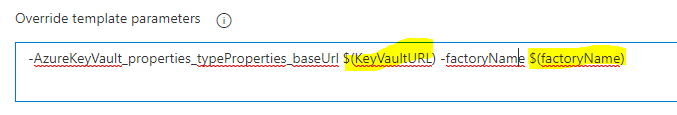
Override parameters section is defined as below, variables $(KeyVaultURL) and $(factoryName) are used from Variable group “Variables-UAT“
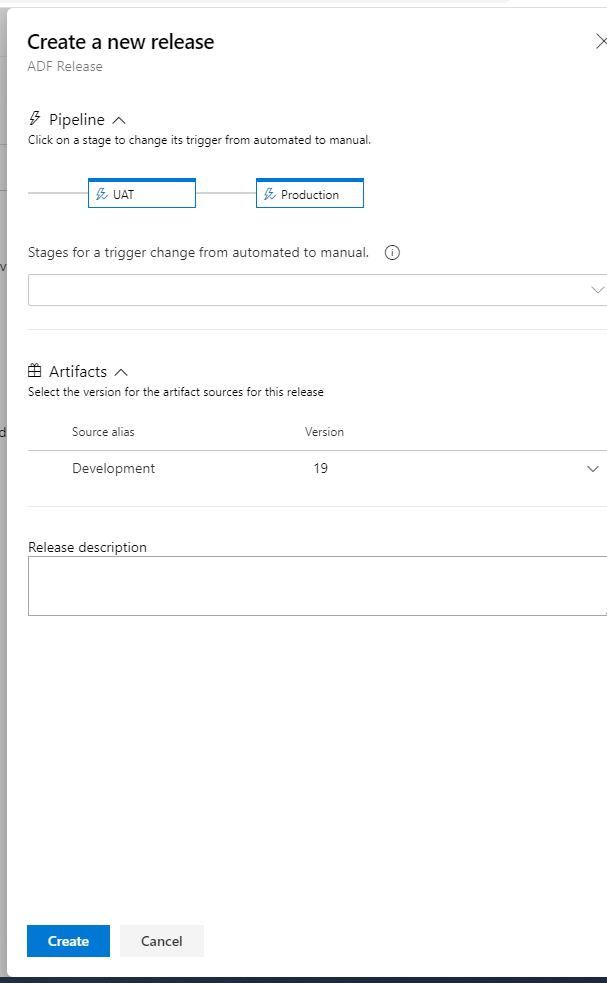
Now we can run UAT deployment – Create release:
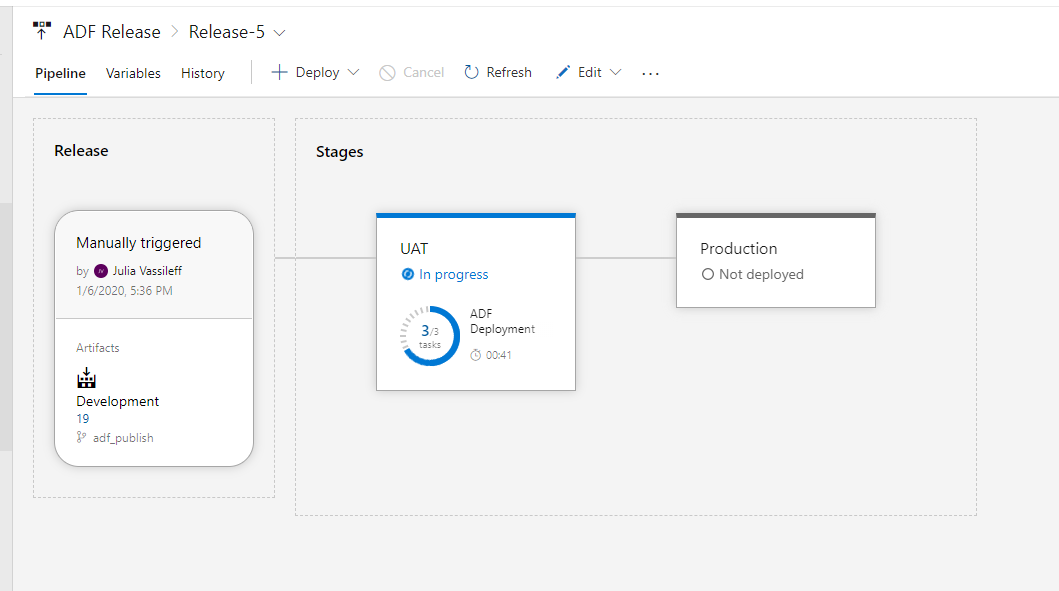
Release is queued and I can monitor the Logs:
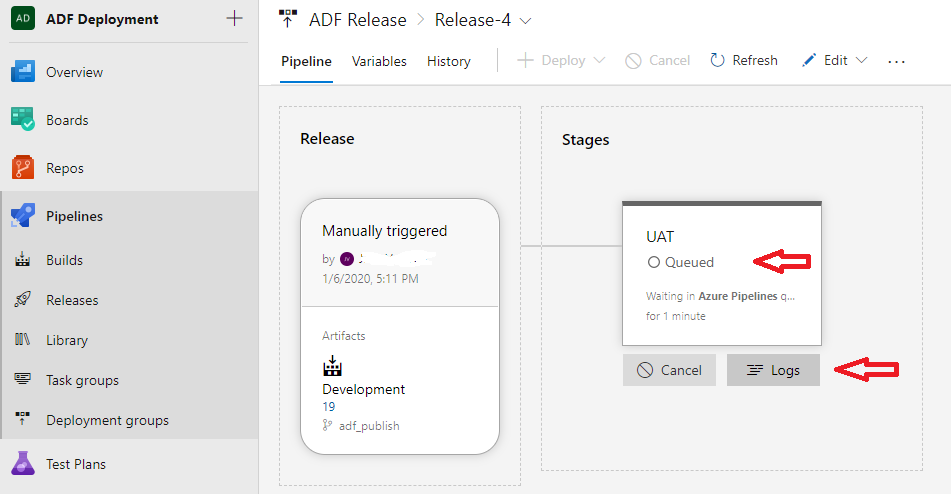
Release is queued and I can monitor the Logs
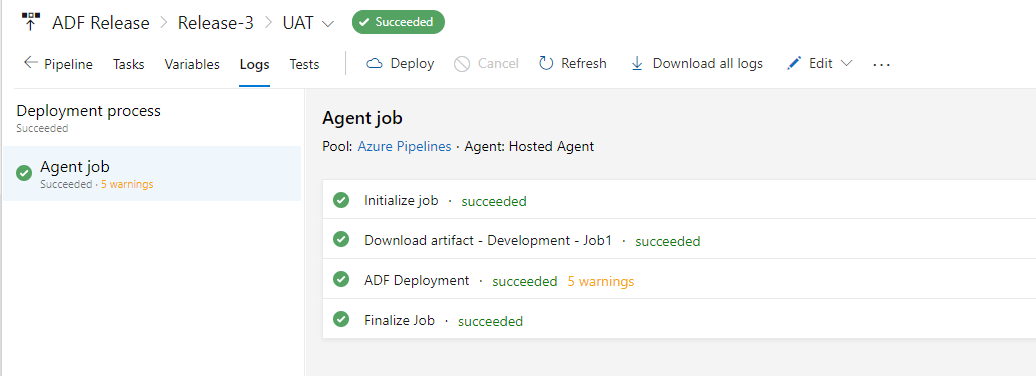
I am checking ADF “adf-demo-uat” to confirm pipeline has been deployed and Key Vault Connection points to UAT Key Vault:
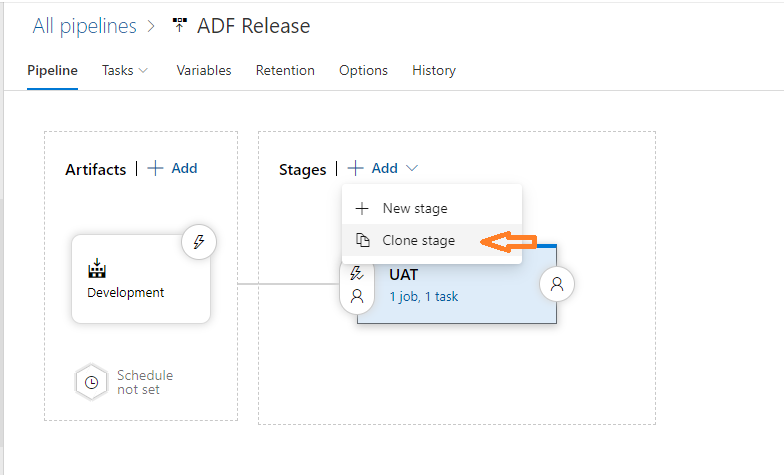
We can now Clone Stage to create a Production deployment.
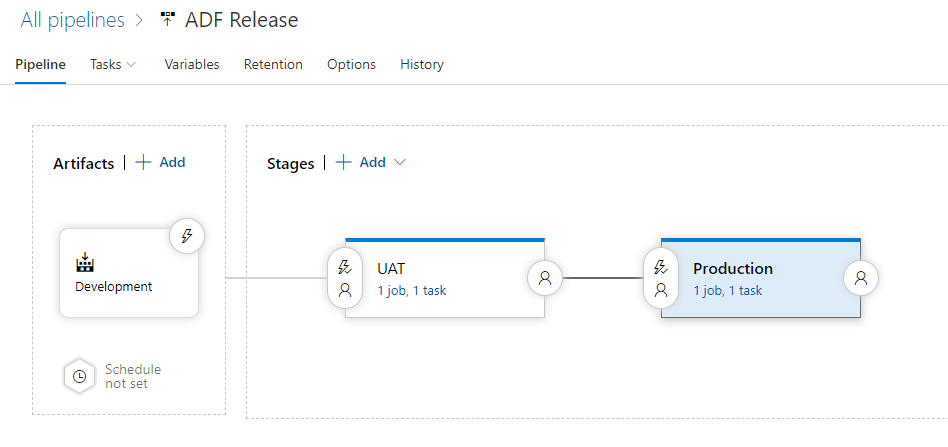
I also add a new Stage scoped Variables group link for Stage “Production“
Let’s now create a new Release:
And monitor deployment progress:
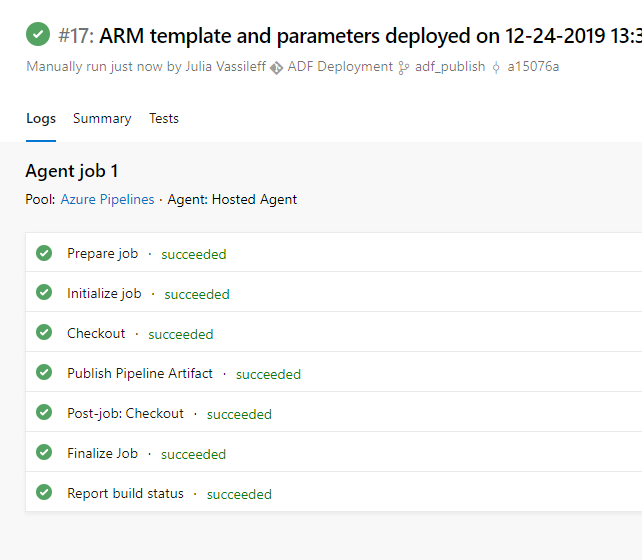
Deployment is successful, I am checking the history:
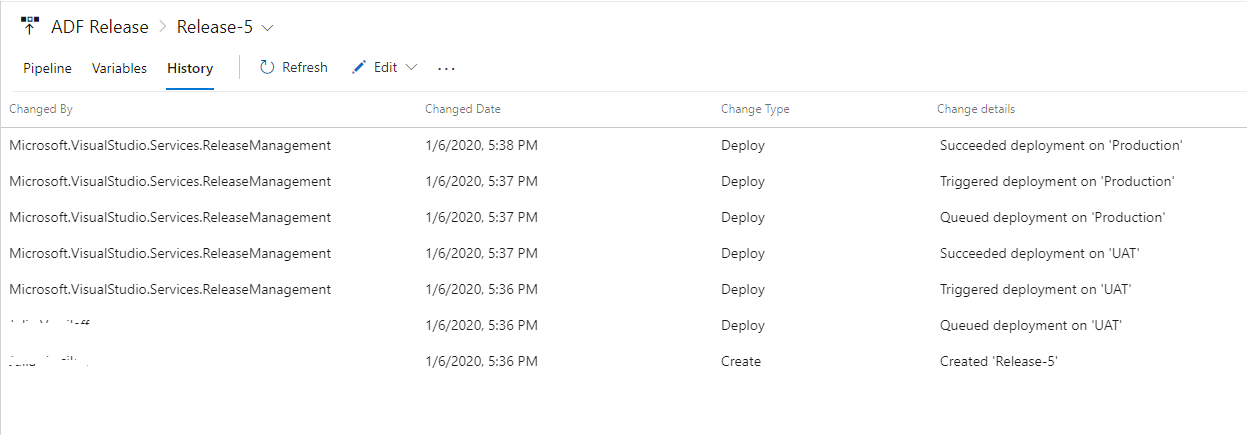
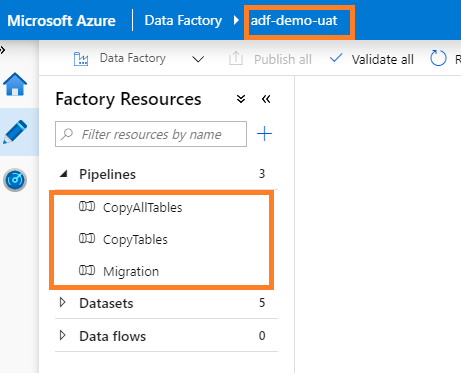
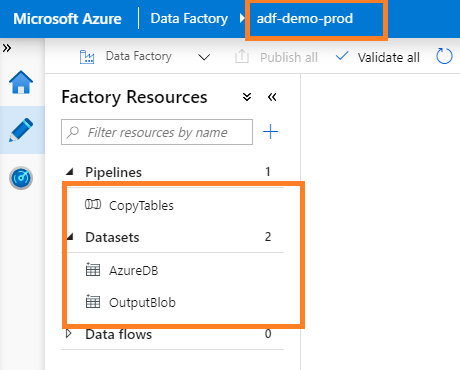
I can confirm deployment in Production ADF:
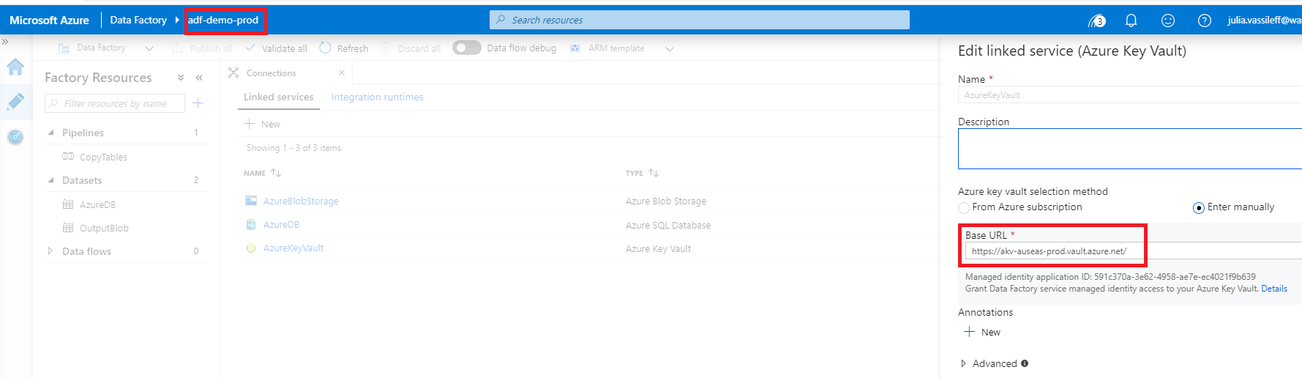
As well as Key Vault Connection points to Production Key Vault:
This concludes this Blog on ADF automated deployment with DevOps.
Optimise your Azure Database
Many organisations notice that moving to the cloud can become expensive, and want to reduce costs.
Traditional IT investments are a capital expense you don’t think about for a couple of years. In this mindset, companies will deploy for the future, and will buy more RAM or CPU for their organization to grow into. However, this way of thinking is not suitable for the cloud. Often, organizations find their bills increasing every month.
WARDY IT Solutions is offering an Azure Database Optimisation Service. We understand IT budgets are finite, so we will look at how you can do more with less.
LEARN MORE

